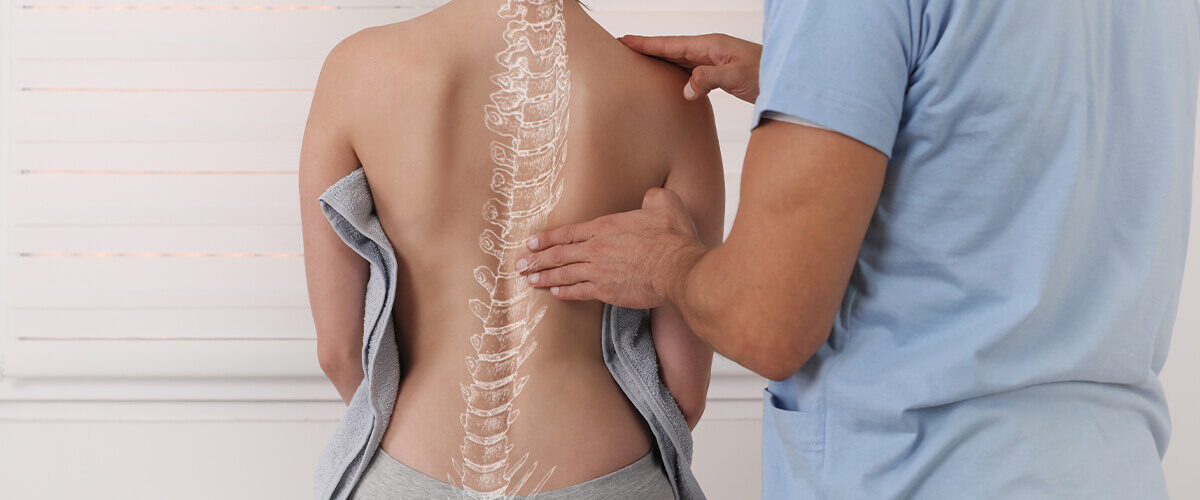
Scoliosis is a sideways curvature of the spine that can occur at any time during the lifetime but more often shows up in adolescents. This condition causes the spine to move to the side, altering the normal posture.
The Scoliosis program offered by physical therapists would be more beneficial as it helps relieve pain, improves spinal mobility, and slows down the curve progression of the spine. They also teach the patients on correct body mechanics and postural awareness.
This article explains scoliosis, its symptoms, causes, and how physical therapy helps improve the quality of patients’ lives.
What is Scoliosis?
The spine is a natural curve structure made up of small bones called vertebrae stacked upon each other. The curve of the spine allows us to bend and move, but with scoliosis, the spine curves more than it should, forming a “C” or “S” shape.
The curve does not affect the appearance or health but can worsen over time, resulting in back pain and other health problems. Some kids are born with scoliosis, while adults can get it later in their life.
The exact cause of scoliosis is unknown, but some believe that it occurs as a result of hereditary factors, as the disorder sometimes runs in families.
Less common types of scoliosis may result from specific neuromuscular conditions, such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy, congenital disorders that affect the development of the spinal bones, spinal cord abnormalities, and infections or injuries in the spine.
Different types of scoliosis exist, and the most common one is adolescent idiopathic scoliosis, in which the lateral curvature comes on for no clear reason and affects children of age 10 to 18. Other types of scoliosis include
- Congenital Scoliosis – A child is born with a lateral curvature of the spine due to a defect in the spinal bones, and the curve becomes more noticeable during growth.
- Neuromuscular Scoliosis – The lateral curvature of the spine results from a neurological or muscular problem. Conditions like cerebral palsy weaken the muscles that support the spine, leading to this type of scoliosis.
- Early-onset Scoliosis – The cause of this type of scoliosis is unknown. Infantile scoliosis occurs below three years of age, whereas juvenile scoliosis is found before age 10.
Symptoms of Scoliosis
Scoliosis does not usually cause pain, but when the lateral curvature of the spine affects the surrounding muscles and joints, it results in pain and changes in posture and movement patterns. The other symptoms of scoliosis include
- Mid or low back pain
- Uneven shoulder or hip height
- Abnormal sensation in the arms or legs
- Difficulty maintaining an upright posture
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Pain with specific movements or activity
How Does Physical Therapy Help with Scoliosis?
Physical therapists develop a custom Scoliosis program according to the type and severity of the condition. The program includes patient education, specific exercises, hands-on methods, and modalities to relieve pain and improve spinal strength.
The Schroth Method
One of the treatments included in the Scoliosis program is the Schroth method, a non-surgical option based on exercises customized according to each patient’s spine curvature. This physical therapy approach benefits patients of all ages regardless of the type or severity of the condition.
This method aims to elongate and stabilize the spine in order to allow the curved spine to return to a more neutral position. The method includes the following factors.
- As the spine curvature affects the muscles in the back, physical therapists suggest specific exercises to restore muscular symmetry.
- Rotational angular breathing techniques to rotate the spine with breathing, thus helping reshape the rib cage and surrounding soft tissue.
- Educating the patients on proper posture, creating awareness to be mindful of the positions that may worsen Scoliosis further.
The Schroth Method of the Scoliosis program helps reduce pain, improves posture, overall movement pattern, and function. It also allows normal breathing in Scoliosis patients.
Other physical therapy treatments include
- Bracing – It helps manage symptoms and limit the progression of spinal curves.
- Heat and Ice Therapy – Heat treatment increases local circulation and relaxes tight muscles, whereas ice therapy decreases pain and inflammation.
- Massage Therapy – Massage performed by licensed therapists increases blood circulation, induces relaxation, and decreases spasms in the tight back muscles.
- Electrical Stimulation – The transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) method helps change the perception of pain by blocking signals to the brain.
- Ultrasound Therapy – This method enhances blood circulation in the deeper tissues, relaxes muscle spasms, and alleviates pain.
Final Thoughts
Physical therapy is an effective and non-invasive treatment for Scoliosis. The Scoliosis program offered at physical therapy centers helps increase muscle strength, improve posture, decrease pain, and educate patients on self-management techniques to control symptoms and limit the progression of the spinal curve.