Who Is At Risk, Diagnosis And Treatment
Chapter 1:
What Is Sudden Blindness?
Chapter 2:
Who Is At Risk Of Sudden Blindness?
Chapter 3:
Causes Of Sudden Loss Of Vision
Chapter 4:
Diagnosis Of Loss Of Vision
Chapter 5:
Treatment Of Sudden Blindness
Chapter 1: What Is Sudden Blindness?
Sudden blindness refers to a medical condition in which a person suddenly experiences difficulty in seeing. As the condition develops, people may start experiencing blurry vision or sudden loss of peripheral or central vision.
People often confuse sudden blindness with complete blindness, but both the conditions are very different from each other. However, if the issue is not addressed in time, sudden blindness may progress, leading to a complete loss of vision.
Sudden blindness may persist for varying durations. For some affected individuals, sudden blindness may ease within a few seconds; for others, it may be hours before their eyesight returns.
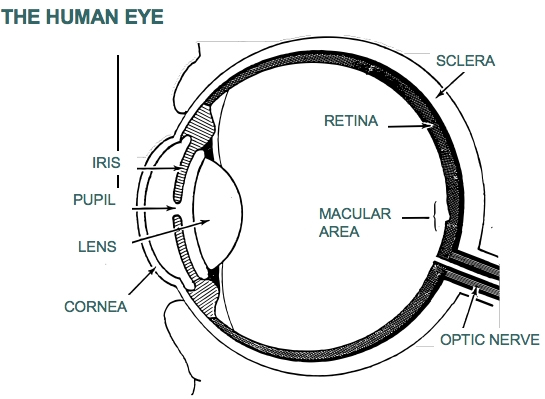
The process of vision involves light passing into the eye and then the retina transmitting the image to the
brain in the form of electrical impulses. Problems in any part of the process may lead to the onset of vision loss. Certain medical conditions such as migraines, retinal vasospasm, closed-angle glaucoma may also lead to a sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes.
FAQs:
Q1. What is sudden blindness?
Sudden blindness refers to a condition characterized by blurry vision or loss of peripheral or central vision.
Q2. What are the causes of sudden blindness?
Several factors can be held responsible for the development of sudden blindness. However, the root causes of sudden loss of vision may include:
- External light sources do not reach your retina.
- The retina is unable to sense light.
- The brain is unable to interpret the impulses sent from the retina
Q3. What are the characteristics of sudden vision loss?
Some of the main characteristics of sudden vision loss include:
- Sudden blindness in one or both eyes.
- Temporary loss of peripheral vision in one eye / both eyes
- Temporary loss of central vision in one or both eyes.
- Sudden onset of blurry vision.
Q4. Is sudden sight loss temporary or permanent?
Sudden vision loss can persist for seconds in some individuals, whereas in others, it can last for hours! However, if not treated on time, this condition may progress into complete blindness.
Q5. How is sudden blindness different from complete blindness?
Sudden blindness is often associated with blurry vision or partial vision loss in one or both eyes. However, complete blindness, on the other hand, means that you lose your ability of sight indefinitely. Seeking treatment immediately can help restore your vision in both scenarios.
Q6. What are the symptoms of sudden blindness in adults?
Common symptoms of sudden blindness in adults are:
- Inability to differentiate between shapes in surroundings.
- Tunnel vision, a condition where peripheral vision is hampered while the central vision is fine.
- Cloudy vision
- Discomfort in the eye, accompanied by any kind of discharge.
Q7. What is an eye stroke?
An eye stroke is commonly known as anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. It is a dangerous condition that may occur as a result of reduced blood flow to the tissues in front of the optic nerve.
Summary:
Sudden blindness may be caused due to several external and internal factors. External factors
impacting the vision may include issues with the image formation in the retina and its
transmission to the brain. Internal factors may include underlying conditions such as
migraines, retinal vasospasm, blood clots and more.
Book an online doctor consultation on MFine to get treated from the best doctors near you!
Chapter 2: Who Is At Risk Of Sudden Blindness?
An individual’s risk of developing sudden blindness can increase due to certain factors.
The risk factors for sudden blindness can be categorized into external and internal, depending on how they affect the individual.
Let us first have a look at the external factors that are a driving force of the causes of sudden loss of vision:
- An Eye Surgery- Those who have undergone an ocular surgery are possibly at higher risk of developing sudden vision loss than the others.
- Occupational Hazards – Individuals who are exposed to sharp or pointed objects at their workplace are at higher risk of incurring eye injuries that may lead to temporary or permanent blindness.
- Poor Hygiene Practices – Individuals with poor hygiene are at greater risk of contracting eye infections making them more susceptible to having eye problems such as sudden loss of vision.
- Lack Of Prenatal Care – Poor nutrition and care during pregnancy can increase the baby’s risk of developing sudden blindness.
- Smoking – Smokers are at greater risk of being affected by sudden blindness as compared to non-smokers.
Some Internal risk factors can also be held responsible for the development of sudden vision loss. Some of them have been mentioned below:
-
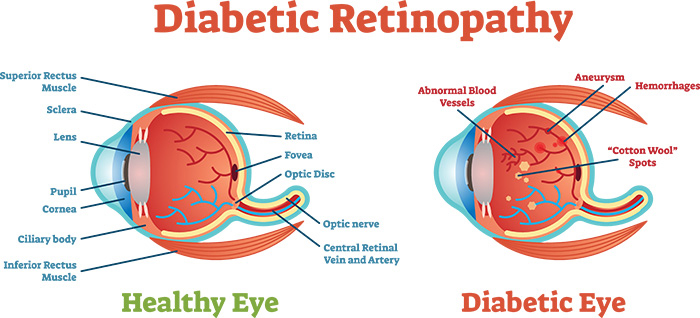
- Diabetes – Diabetes is a condition that leads to the onset of various other ailments in the body. Diabetic people are at greater risk of suffering from sudden blindness and other eye-related problems as compared to non-diabetics.
- Cerebrovascular Or Cardiovascular Diseases – People suffering from cardiovascular problems may develop blood clots that may hamper their vision. Such people are more susceptible to developing eye-related ailments and sudden blindness.
- Stroke – Individuals who have previously had a stroke are also at greater risk of losing their vision.
- Pre-Existing Eye Diseases – People who are already combating eye diseases are at a higher risk of developing sudden blindness.
- Poor Nutrition – Those who do not eat a well-balanced nutritious diet tend to develop disorders that can impact their eyesight and eventually lead to loss of vision.
- Premature Birth – Babies born prematurely have been observed to be at a higher risk of developing sudden blindness
- Family History – A person with a family history of partial or complete blindness, is at higher risk of developing the same condition at some point in his/herlife.
- Advancing Age – Older adults tend to be at high risk of being affected by the sudden loss of vision.
Internal and external factors play a significant role in increasing an individual’s risk of developing sudden blindness. Hence, if you can relate to any of the above factors, better watch out for even the minutest signs of vision loss and immediately avail treatment.
FAQs:
Q1. Can an individual’s work environment contribute to loss of vision?
Yes, if an individual’s job involves working with or getting exposed to sharp objects or toxic chemicals, their chances of developing sudden blindness increase significantly.
Q2. Can diabetes cause temporary loss of vision in one or both eyes?
As diabetes progresses, it may damage eyes causing conditions such as diabetic retinopathy macular
edema, cataract etc. All these conditions may cause temporary loss of vision in one or both eyes. If diabetes is left untreated, it can also lead to permanent loss of vision.
Q3. Does genetics play a role in the onset of sudden blindness?
Like in many other health conditions, genetics plays a significant role in the development of sudden blindness. Thus, if your parents have a history of sudden or complete blindness in the past, your chances of developing it are also quite high.
Q4. What factors cause sudden, painful unilateral vision loss?
Health conditions like stroke, migraines, and eye diseases like cataracts, acute onset glaucoma and closed-angle glaucoma are common causes associated with unilateral vision loss or sudden loss of vision in one eye. A blood clot or reduced blood flow to the eyes are also often observed to cause sudden unilateral vision loss.
Q5. Why are older adults at higher risk of developing sudden vision loss?
Advancing age causes all the functions in one’s body to slow down and deteriorate. Thus, an individual’s eyesight is also ought to deteriorate with advancing age, which becomes a contributing factor to the development of sudden vision deterioration.
Q6. Does your diet play a role in the onset of sudden blindness?
A healthy and well-balanced diet is crucial for all the organs in your body. A diet that lacks significant nutrients can lead to various health disorders, including poor vision.
Q7. What follows sudden sight loss in one eye?
Individuals who face a sudden sight loss in one eye tend to lose a part of their side vision. Initially, they may experience problems with depth perception. Studies indicate that adults who end up losing vision in one eye may also experience a decrease in their ability to accurately judge distances and track movements.
Summary:
The risk of developing sudden blindness may increase due to several factors such as eye surgery, poor hygiene practices, smoking, genetics, age, etc. If a person notices any symptoms related to vision loss, an ophthalmologist must be immediately consulted, Any delays in addressing the issue may lead to increased complications.
Consult a top ophthalmologist on MFine to know more!
Chapter 3: Causes Of Sudden Loss Of Vision
There are several causes of sudden loss of vision. Certain conditions can cause either sudden partial blindness (in which you can detect light and shapes) or sudden complete blindness (when you cannot detect light and cannot see anything). Many of these factors are temporary and can be resolved through timely medical intervention. Some conditions, however, are more serious and are potentially irreversible.
Causes of Sudden Loss of Vision: Partial Blindness
The are several factors that trigger the onset of sudden vision loss in one or both eyes. Here are some of the causes of sudden loss of vision: :
- Migraines (reversible)- These throbbing headaches have time and again reported to cause painful vision loss in one or both eyes. They are one of the major causes of temporary partial vision loss. The loss of vision caused by migraines is characterized by sensing flashlights or seeing blind spots.
- Retinal Migraine (reversible)- A type of migraine called retinal migraine is sometimes associated with the onset of sudden blindness in one eye. This is called an ‘aura’ and usually affects only one eye. Once it occurs, the affected individual may lose sight in one of their eyes for about 20 minutes. This can occur right before or even during a migraine.
- Closed-Angle Glaucoma (reversible)- Yet another leading cause of sudden blindness in one of the eyes is closed-angle glaucoma. This condition is mostly associated with loss of vision in just one eye due to excessive pressure caused by a bulging iris. The pressure from the iris prevents drainage of the eye fluid, which, in turn, can lead to a host of different problems like pain in the eye and loss of vision. Permanent vision loss is a possibility if closed-angle glaucoma isn’t diagnosed and treated on time.
- Retinal Vasospasm (reversible)- This condition negatively impacts the flow of blood to the retina. As a result, it may cause a temporary partial loss of vision. Retinal vasospasm causes the blood vessels in your retina to tighten.
- Severe Preeclampsia (reversible) – Sudden vision loss or changes in the vision occur in very serious cases of preeclampsia. Sudden loss of vision can be a sign of something more serious like swelling of the brain or an issue with the central nervous system.
If you experience sudden vision loss during your pregnancy (especially if you have already been diagnosed with preeclampsia), make sure you get medical help immediately.
- Giant Cell Arteritis (potentially irreversible)- Another common cause of temporary vision loss is giant cell arteritis. This condition is a common cause of loss of vision in adults over 50 years of age. If this condition is left untreated, it is known to cause permanent or chronic sudden blindness.
- Retinal Detachment (potentially irreversible) – Retinal detachment is a condition in which the retina moves away from its normal position. When this happens, blood flow to the retinal tissues is blocked, thus, if the condition isn’t treated immediately, it can result in permanent blindness. There are a number of causes of retinal detachment. In diabetic patients, the creation of scar tissue can cause the retina to detach. In some cases, fluid accumulation due to injury can lead to retinal detachment.
Causes of Sudden Loss of Vision: Complete Blindness
- Vitreous Haemorrhage (reversible) – Sudden blindness can also be caused by vitreous hemorrhage where blood leakage occurs. This leakage blocks light and doesn’t allow it to enter the eye, making it difficult for the affected individual to see anything.
- Retinal Vein Occlusion (potentially irreversible) – When the flow of blood to the vein is blocked due to a blood clot or any other factor, it is known as retinal vein occlusion. The blockage of blood supply to the retina can starve the tissues of oxygen and nutrients and is a very serious condition. If left untreated for too long, it can result in permanent blindness.
The conditions mentioned above were some of the most common causes of sudden vision loss. Let us now have a look at some rare causes that may contribute to the onset of sudden blindness. They include:
- Epileptic Seizures (reversible) – While seizures are commonly associated with physical seizures, you may be surprised to know that epileptic seizures can also contribute to sudden blindness in rare cases. About 10 % of people suffering from this condition can have their occipital lobe impacted. This impact can cause loss of vision during or after the seizure.
- Uhthoff Phenomenon (reversible) – This is another rare cause of sudden vision loss. It often affects those who have multiple sclerosis. Some individuals may experience an increase in their body temperature due to multiple sclerosis, causing them to become temporarily blind in one or both eyes.
FAQs:
Q1. What is Amaurosis Fugax?
Amaurosis Fugax is a medical condition that causes an individual to lose eyesight in one or both the eyes due to a lack of blood flow. It is often caused by underlying conditions such as blood clots or lack of blood flow to the blood vessels present in the eye.
Q2. Can migraines cause a temporary partial loss of vision in one eye?
Yes, migraines are the number one cause of sudden vision loss in one or both eyes for many. It usually leads to temporary loss of vision in one eye that is characterized by sensing flashlights or sighting blind spots. Blindness triggered by migraines can occur right before or even during a migraine.
Q3. What are the causes of sudden loss of vision in a child?
The causes of sudden vision loss in children is similar to that in adults. Migraines, blood clots, retinal vein occlusion, and seizures are associated with loss of vision in children just like in adults. Additionally, poor nutrition, inadequate prenatal care, premature birth, and a family history of sudden blindness can also trigger a sudden vision loss.
Q4. How do individuals battling epileptic seizures develop sudden vision loss?
About 10% of the individuals suffering from epileptic seizures develop problems within the occipital lobe. These issues are known to result in sudden blindness in some of the affected people. The onset of sudden vision loss may occur during or after a seizure.
Q5. What is the most common cause of sudden vision loss?
The most common cause of sudden blindness is a migraine headache. These throbbing headaches are reported to cause vision loss in one or both eyes. They are one of the main causes of temporary partial vision loss. The loss of vision caused by migraines is characterized by sensing flashlights or seeing blind spots. Other common causes of sudden vision loss include giant cell arteritis, retinal vasospasm, closed-angle glaucoma, and vitreous hemorrhage.
Q6. How do blood clots cause sudden blindness?
The formation of a blood clot can cause sudden temporary loss of vision in one eye or both eyes. If the required treatment is not availed in time, this condition may result in permanent loss of vision. The clot can either develop in the retinal artery or any other blood vessel, which goes on to cloud your vision and eventually leads to complete loss of vision.
Q7. What is vitreous hemorrhage?
Vitreous hemorrhage is a condition where blood leakage occurs in the eye. This leakage causes blockage of light and doesn’t allow it to enter the cornea, making it difficult for the affected individual to see clearly.
Summary:
Sudden vision loss may have several underlying causes such as various health conditions (migraines, Giant Cell Arteries, Closed Angle Glaucoma, Vitreous Hemorrhage, etc. Loss of vision may also be attributed to reduced blood flow, blood clots in arteries, and more.
Get tested by consulting a top ophthalmologist on MFine!
Chapter 4: Diagnosis Of Loss Of Vision
The onset of sudden blindness must be immediately followed by prompt diagnosis and treatment to avoid further complications. To prescribe the right treatment, your physician may first advise undergoing any of the following diagnostic analysis.
Retinal examination:
During a retinal examination, your ophthalmologist will examine your retina and the blood supply to it to identify any underlying issues. This type of examination is usually done using an ophthalmoscope after your pupils have been dilated. While there could be several causes of sudden loss of vision, If the reason behind your sudden vision loss is due to an issue with the retina, then this procedure can identify it.
Intraocular pressure:
An examination of intraocular pressure evaluates the fluid pressure within the eye. This procedure is usually performed to identify or confirm a diagnosis of glaucoma in a patient.
Ultrasound assessment:
Ultrasonography may be prescribed for analyzing the functioning of your eyes. This will provide an extremely detailed view of your eye and socket. A
Gadolinium-enhanced MRI:
This diagnostic analysis may be performed for detecting the possible cause of sudden blindness. This method uses
gadolinium to improve the clarity of images produced by Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
Biomicroscopy Test:
Your physician might prescribe this test to inspect the general health of your eyes. It is also known as a Slit Lamp examination. In this procedure, the ophthalmologist might use eye drops to dilate your pupils or drops containing a yellow dye which can help them identify abnormalities in the cornea. After this, the doctor will examine your eyes using a microscope and a slit lamp. A biomicroscopy test can help identify corneal injuries, retinal detachment, blockages, or macular degeneration.
Blood Tests:
Blood tests that measure Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate measure how quickly erythrocytes or red blood cells settle. If the cells are observed to settle faster than usual, it indicates inflammation in the body. Another blood test prescribed for those with sudden blindness is to measure the level of C-reactive protein in the blood. This substance is produced in the blood in response to inflammation in the body.
In addition to these diagnoses, an ophthalmologist may also conduct a general physical examination of the affected eye to determine the cause.
During a physical examination, each of your eyes will be checked separately. Your doctor will then check your
eyesight by analyzing how far and how clearly you can see. The functionality of your eye muscles and pupils will also
be checked with the tests described above.
FAQs:
Q1. Why is sonography used for diagnosing sudden blindness?
Eye sonography or ultrasound helps in creating images of the internal eye to detect the underlying cause of sudden blindness. Sonography, along with an MRI scan, may help in determining causes of sudden blindness such as Amaurosis Fugax. This differential diagnosis used for the detection of Amaurosis Fugax may also help in identifying damage and blockages of the blood vessels in the eye that causes sudden loss of vision in one eye.
Q2. How is gadolinium-enhanced MRI different from a usual MRI?
A gadolinium-enhanced MRI helps in producing clearer images as compared to a normal MRI. Thus, it helps in detecting issues with the eye in a lot better way.
Q3. What does the Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) help determine?
ESR blood test helps detect the presence of inflammation in the body. If the ESR is normal, it means there is no apparent inflammation in the body. On the other hand, if the ESR is higher than normal, it is an indicator of inflammation, which may hint at a potential underlying cause of sudden blindness.
Q4. What are the common diagnostic approaches for detecting sudden blindness?
Some of the common diagnostic procedures for determining the cause of the onset of sudden vision loss include:
- Sonography
- Gadolinium-enhanced MRI
- Blood tests to detect ESR and C-reactive protein
- Biomicroscopy test
- Physical examination
Q5. How does an ophthalmologist diagnose sudden blindness?
An ophthalmologist may begin by conducting a physical examination of the eyes and then asking the patients to undergo certain diagnostic tests (imaging and blood tests). After carefully looking at the test results, the ophthalmologist may reach to a conclusion on whether or not a person is suffering from sudden blindness.
Q6. Should I wait for my vision to return on its own?
The eye is a precious organ. If you are experiencing a sudden vision loss for the first time, it would be better to get immediate medical help in order to intervene quickly.
Q7. What is a biomicroscopy test?
A biomicroscopy test is commonly referred to as a slit lamp test. Your eyes can be analyzed at a microscopic level with the help of this test. It helps an ophthalmologist quickly detect abnormalities with your eyes such as corneal injury, cataract, macular degeneration, detached retina, and retina vessel blockage.
Summary:
Diagnosis of sudden blindness includes both imaging and blood tests such as ultrasonography, gadolinium-enhanced MRI, Erythrocytes Sedimentation Rate, C-reactive protein level test, and more.
To get diagnosed for a sudden vision loss, consult a top ophthalmologist on MFine
Chapter 5: Treatment Of Sudden Blindness
Once the reason behind loss of vision is successfully determined, no time should be wasted in availing appropriate treatment for the condition. Your doctor will create a personalized treatment depending upon your present health condition:
Some of the most common treatments prescribed for sudden blindness include:
- Wearing Eyeglasses – If the blurry vision is being caused due to a refractive error your ophthalmologist may prescribe corrective glasses to restore your vision.
- Medications – When your vision loss is due to an underlying infection, the doctor may prescribe certain medications to restore your vision. You may also be prescribed medications to treat the inflammation that could be blocking the blood vessels in the eye and impairing your vision.
Treatment for reversible blindness:
(i) Preeclampsia: Treatment of sudden vision loss due to preeclampsia will involve treatment of the condition itself. Since vision loss is a characteristic of advanced preeclampsia, vision should return once the condition is brought under control. If the fetus is ready to be delivered, then this is the best option to treat preeclampsia. Otherwise, medication to reduce blood pressure can be prescribed.
(ii) Vitreous Haemorrhage: The first step in treating vitreous hemorrhage is to find the source of the bleeding. Once this has been identified, laser treatment can be done to repair any damaged vessels and stem the flow.
Treatment for irreversible blindness:
If the cause of sudden vision loss is irreversible, doctors might have to take more extreme measures to treat the condition or minimize damage. Treatment will depend on the condition and the extent of the damage. Listed below are some common reasons for irreversible sudden blindness and their treatment.
(i) Glaucoma: Treatment for glaucoma will depend upon the severity of the case. If the condition is caught early on, eye drops to reduce fluid buildup in the eye will be prescribed. Commonly prescribed eye drops include prostaglandins (which increase fluid secretion), beta-blockers (which reduce fluid production), and rho kinase inhibitors (which reduce the effect of rho kinase enzymes that can contribute to pressure buildup). In case the eye drops aren’t effective, you might be prescribed oral medication to reduce fluid production. If medication also does not produce the desired effect, your doctor might have to resort to surgical treatment or laser therapy
(ii) Corneal Damage: If the cause of sudden vision loss is injury resulting in severe damage to
the cornea, a laser treatment to remove the scar tissue and reshape the cornea might be required.
This treatment is known as phototherapeutic keratectomy. In extreme cases where the cornea cannot be treated, a corneal transplant surgery might be required to restore vision.
(iii) Retinal Vein Occlusion: If the cause of sudden loss of vision is a blood clot or some other kind of blockage, the doctor can only minimize the damage, but not reverse the blockage. Injections like steroid injections or vascular endothelial growth factor can reduce fluid buildup and improve your vision. In some cases, laser treatment to seal off veins and block the flow of fluids to the eye might be required.
To get the most effective diagnosis and treatment, you must consult an ophthalmologist as soon as the symptoms become noticeable This will help in determining the root cause of the condition. Delay in availing the treatment can lead to more complications where an individual’s risk of developing permanent blindness may increase manifold.
How to cope with sudden blindness
In severe cases where blindness is irreversible, it can be difficult to get accustomed to having limited vision. Living with partial or complete blindness requires a person to reorder their lives and learn new skills. Here are a few coping strategies that can come in useful.
(i) Rearrange your home: If a loved one has been diagnosed with sudden irreversible blindness, the first step you need to take is to rearrange your furniture to make moving around easier. Make sure there are wide passageways with nothing blocking them. You should also keep small toys or other objects out of the way to prevent accidents.
(ii) Install railings wherever needed: Railings are an important safety measure to take if a loved one is experiencing blindness. They can make it easier for them to move around and be more independent within the house.
If you have long passageways, install a railing on the side. You should also install a railing next to the toilet and the shower. Of course, it goes without saying that if you have a staircase within your home, railings are a must. You can even install railings on both sides to make moving around safer.
(iii) Make full use of voice technology: Getting diagnosed with sudden blindness doesn’t mean saying goodbye to favorite hobbies. Technological advancements have led to the development of voice technology, which is very helpful for the visually challenged. Audiobooks, voice commands on smartphones, and voice-powered virtual assistants can make it a little easier to live with blindness.
(iv) Join a support group: Sudden blindness can come as a complete shock because of how abruptly it occurs. The psychological and emotional impact can be just as severe as physical trauma. Support groups are a wonderful way to connect with people who have gone through similar experiences and learn from them.
FAQs:
Q1. Can medications treat sudden blindness?
Yes, medications are usually prescribed to treat sudden blindness. If your vision loss is caused by medical conditions such as diabetes, stroke, blood clot, or other such health issues, medications may significantly help improve your vision.
Q2. Is surgery the last resort for restoring vision loss caused by sudden blindness?
If your loss of vision is triggered by cataract or blood clots that need to be removed, surgery may be the only option guaranteed to restore your vision. However, it would be your medical practitioner who is going to decide whether or not to undergo surgery.
Q3. How to treat sudden blindness in children?
If you find your child having vision problems, it is best to take him/her to the ophthalmologist without any delays. Proper diagnostic tests and medications will help your child regain the vision and alleviate the associated symptoms.
Q4. Can you prevent sudden blindness?
Regular eye checkups can help you keep track of your health. Eating a nutritious diet can also improve your overall health and reduce the risk of nutritional deficiencies that can lead to sudden blindness. If you have a pre-existing condition like diabetes, then make sure you manage it properly to avoid complications like sudden blindness.
Q5. Can lifestyle changes help treat sudden blindness?
Yes, positive changes to your lifestyle can significantly impact sudden blindness. Making sure that you eat healthily, exercise regularly, and reduce stress levels to be able to tackle vision loss. If you have diabetes, you must control your sugar intake. Obese individuals must try their best to get back in shape with a normal BMI. If you are a smoker, quit smoking as it is also considered a serious risk factor for developing sudden blindness.
Q6. What is legal blindness?
Someone who is legally blind has a corrected vision of 20/200 or 6/60 in their best-seeing eye, after correction with glasses, which simply means that despite best efforts with prescription glasses, vision does not improve beyond 20/200 or 6/60. Blind in one eye but with a normal other eye is not legal blindness. But people with legal blindness have corrected vision. They can see to some extent from one or both eyes.
Summary:
– Sudden loss of vision is a serious concern. In case of such an event, once the cause is detected, the patient should consult with an ophthalmologist at the earliest. He/she would be able to find the root cause and prevent any possible further damage.
– A legally blind person is a term used for loss of vision that isn’t restored despite undergoing treatment like surgery.
You can consult a top ophthalmologist on MFine to get the best treatment for sudden loss of vision!

