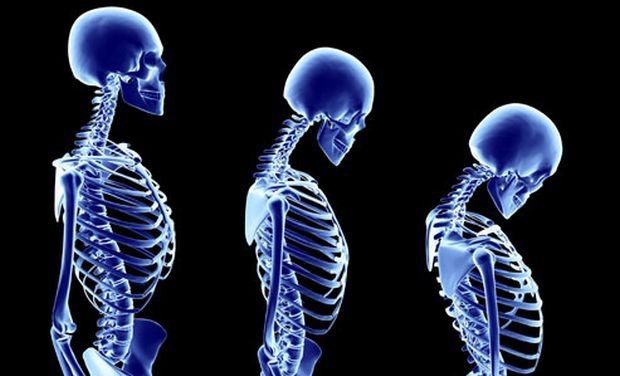
Skeletons in your closet is a well-known phrase. Just like you shouldn’t keep your thoughts bottled up to keep your mental health at its best, you should also take care of your bone health by regularly visiting your Orthopedician when you start ageing.
When we used to see the famous skeleton hanging in our biology lab, we never thought it serves so many purposes in our bodies.
Functions of Bones:
- Provide a frame that supports our body on which muscles, tendons, and ligaments attach. It will be difficult to move if our body didn’t have bones. Just like Earthworms.
- Protect vital organs of our body like, the skull protects the brain and our ribs guard the heart and lungs against external injury
- Spongy bones present at the end of our long bones (arms and legs) contain bone marrow that produces our blood cells and platelets
- They are made of a honeycomb-like structure that stores minerals like calcium and phosphorus
- Bones also have a lesser-known function. They help us to maintain pH of the blood by releasing or absorbing alkaline (basic) minerals
- They are a reservoir of calcium and can increase levels of calcium in the blood by releasing stored calcium or decrease its levels by absorbing it
How do Bones Function and Form?
Until we turn 30, our body ensures that an equal amount of old bones are being removed as the new ones are forming. After a certain age, when levels of sex hormones in males and females start decreasing, the formation of new bones gets slower. Lastly, the rate of removal of old bones is higher than the formation of new bones.
Factors affecting the decline in bone mass in combination with Aging:
- Alternate levels of hormones
- Nutrition: Consuming a low Calcium and Vitamin D diet
- Lack of physical activity
- Comorbid medical conditions like malnutrition, mineral disorders, and anaemia
- Certain medicines such as steroids, and medicines used to treat female sterility
- Female gender: When females reach menopause, estrogen levels in the body get low which increases bone resorption (breaking down old bones), and reduce forming new bones and overall, bone loss is sped up.
- Smoking: It causes hormonal imbalances which cause the development of co-morbid conditions, and bone loss
The most common bone disease related to ageing is osteoporosis, followed by osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Osteomalacia. Due to bone loss, the bone becomes fragile which causes them to break easily, joints become painful and stiff, movement becomes slow or limited, and strength of muscles reduces. Also, the pattern of walking gets slower and shorter which causes difficulty in walking which causes tiredness on walking even for a small distance.
Prevention of Ageing-related Bone Diseases:
- Consume a diet rich in calcium which includes yoghurt, green leafy vegetables, tofu, milk, and curd
- Consume a diet rich in Vitamin D which includes eggs, mushrooms, and milk. Seafood such as tuna, oysters, and salmon is also abundant in Vitamin D
- Perform regular physical activity
- Get a regular bone mineral density test so that early intervention can take place
- Get levels of calcium and Vitamin D checked and take supplements (under the physician’s advice) if you are deficient.
There are no symptoms associated with bone disease and hence, it goes unnoticed but it increases the risk of fracture which restricts movement and may result in various conditions, including Deep Vein Thrombosis.

Manage your health and reduce the chances of the development of health-related complications. Download the Zyla app (http://bit.ly/2BftxyE-defeatingdiabetes) for continuous monitoring and personalised care.
For more information, you can visit here