In today’s industrial landscape, where energy costs are soaring and environmental concerns are at the forefront, maximizing boiler efficiency has become a top priority for facility managers and operators. Boilers are essential components of many industrial processes, providing heat and steam for various applications. However, inefficient boiler operation can result in significant energy waste, increased greenhouse gas emissions, and higher operational costs. By implementing effective boiler efficiency strategies, industries can reduce their energy consumption and carbon footprint and potentially realize substantial cost savings. This comprehensive guide explores practical strategies that boiler users can adopt to maximize energy efficiency and achieve sustainable, cost-effective operations.

Conduct Regular Boiler
Maintenance Proper maintenance is the cornerstone of boiler efficiency. Regular inspections, cleaning, and tune-ups can ensure that your boiler operates at peak performance, minimizing energy losses and extending its lifespan. Establish a comprehensive maintenance schedule that includes tasks such as:
- Cleaning heat transfer surfaces (fireside and waterside)
- Inspecting and replacing worn or damaged components
- Checking and adjusting burner settings for optimal combustion
- Monitoring and calibrating control systems
- Checking for leaks and insulation integrity
Neglecting maintenance can lead to scale buildup, fouling, and inefficient combustion, all of which contribute to increased energy consumption and higher operating costs.
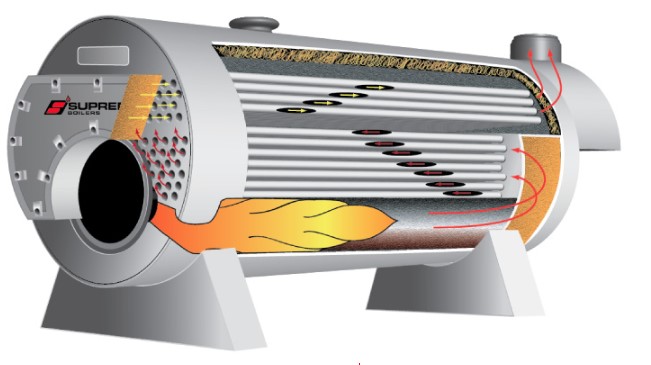
Optimize Boiler Loading and Cycling
Efficiency losses can occur when boilers operate at low loads or cycle frequently. To minimize these losses, it’s essential to optimize boiler loading and cycling practices. Consider implementing the following strategies:
- Match boiler capacity to your facility’s steam or hot water demand as closely as possible. Oversized boilers operating at low loads are inherently less efficient.
- Utilize multiple smaller boilers instead of a single large boiler to better match varying load conditions.
- Implement load-sharing strategies to distribute the load evenly across multiple boilers.
- Minimize cycling by optimizing boiler setpoints and employing techniques like load shedding or thermal storage.
By reducing low-load operation and excessive cycling, you can significantly improve boiler efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
Implement Combustion
Optimization and Control Systems Efficient combustion is crucial for maximizing boiler efficiency. Combustion optimization involves precisely controlling the air-fuel ratio, ensuring complete combustion, and minimizing excess air. Advanced combustion control systems, such as oxygen trim systems or parallel positioning controls, can automatically adjust air and fuel flows based on real-time feedback, maintaining optimal combustion conditions and reducing energy losses.
Additionally, implementing boiler control systems that integrate with your facility’s energy management system can help optimize boiler operation based on varying load demands, further enhancing efficiency.
Recover and Utilize Waste Heat
Boilers inherently generate waste heat that is often discharged into the environment through flue gases, blowdown, and other sources. Recovering and utilizing this waste heat can significantly improve overall system efficiency and reduce energy consumption. Consider implementing the following strategies:
- Install economizers or air preheaters to recover heat from flue gases and preheat the combustion air or boiler feedwater.
- Implement condensing heat recovery systems to capture the latent heat from flue gas condensation.
- Utilize blowdown heat recovery systems to preheat makeup water or other process streams.
- Explore opportunities for cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP) systems, where waste heat is used to generate electricity or provide process heating.
By capturing and utilizing waste heat, you can reduce the energy input required for your boiler system, resulting in substantial energy savings and improved overall efficiency.
Upgrade to High-Efficiency Boiler
Technologies If your existing boiler system is outdated or approaching the end of its useful life, consider upgrading to newer, more efficient boiler technologies. Modern boiler designs, such as condensing boilers, fluidized bed combustion (FBC) boilers, or supercritical boilers, offer significantly higher thermal efficiencies compared to traditional boiler types. Additionally, these advanced technologies often incorporate improved emission control systems, contributing to a lower environmental impact.
While the initial investment in a new boiler system may be higher, the long-term energy savings and reduced operating costs can offset the upfront costs, making it a financially viable option, especially when factoring in potential incentives or rebates for energy-efficient upgrades.
Implement Energy Monitoring and Management
Systems Continuous monitoring and data-driven decision-making are essential for maximizing boiler efficiency. Implement energy monitoring systems that track key performance indicators, such as fuel consumption, steam or hot water production, and efficiency metrics. These systems can provide valuable insights into your boiler’s operation, enabling you to identify inefficiencies, track the impact of efficiency measures, and make data-driven adjustments.
Furthermore, integrating your boiler system with a comprehensive energy management system can help optimize overall facility energy use, enabling you to make informed decisions based on real-time data and predictive analytics.
Explore Alternative Fuel Sources
Depending on your location and industry, exploring alternative fuel sources for your boiler system can potentially improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Biomass fuels, such as wood pellets or agricultural waste, can be a renewable and carbon-neutral alternative to fossil fuels. Additionally, some boiler technologies, like fluidized bed combustion (FBC) boilers, are designed to handle a wide range of fuel types, including low-grade coals and waste materials.
Switching to alternative fuels may require modifications to your boiler system or even a complete system replacement. However, the potential benefits in terms of efficiency, cost savings, and reduced emissions may make it a worthwhile investment, particularly in regions with favorable incentives or regulations promoting sustainable energy sources.
Foster a Culture of Energy Efficiency
Maximizing boiler efficiency is not solely a technological endeavor; it also requires a cultural shift within your organization. Foster a culture of energy efficiency by:
- Providing regular training and awareness programs for operators and maintenance personnel on best practices for boiler operation and energy conservation.
- Establishing clear energy efficiency goals and incentives for meeting those targets.
- Encouraging collaboration and communication between various departments (operations, maintenance, and energy management) to identify and address inefficiencies.
- Promoting continuous improvement and innovation in energy-efficient practices and technologies.
By fostering a culture of energy efficiency, you can ensure that all stakeholders are aligned and committed to maximizing boiler performance and reducing energy waste.
The EASCO SM4 Series: Supreme Boilers’ Compact Powerhouse
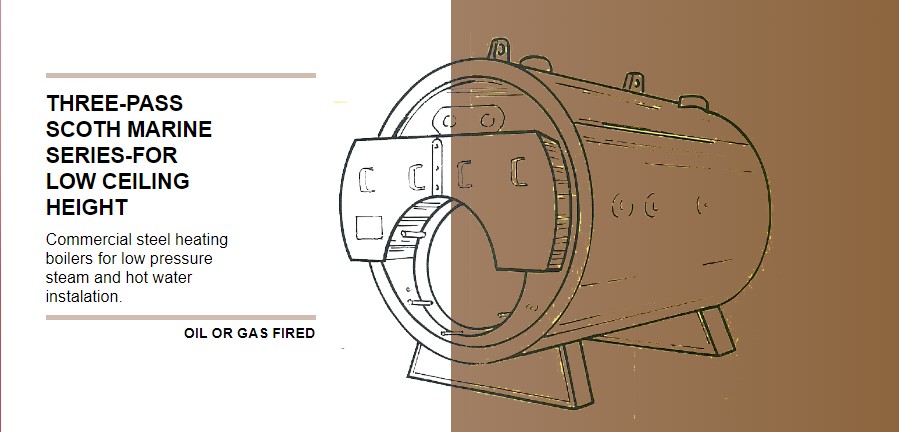
For facilities seeking a space-efficient and high-performance heating solution, Supreme Boilers’ EASCO SM4 Series offers a compelling proposition. This line of three-pass Scotch marine boilers is engineered specifically for commercial steel heating applications where vertical clearance is limited. Designed with energy efficiency in mind, the EASCO SM4 Series boasts an impressive five square feet of fireside heating surface per boiler horsepower, contributing to a fully rated output with quiet operation. The innovative 2.5-inch fire tubes eliminate the need for turbulators or baffling, ensuring balanced flue gas flow and optimum heat transfer. Available in both oil and gas-fired configurations, these boilers can be seamlessly integrated into low-pressure steam or hot water installations. Constructed with meticulous attention to detail, including gas-tight front and rear smoke boxes, wet back construction, and adherence to ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code standards, the EASCO SM4 Series exemplifies Supreme Boilers’ commitment to quality and performance in a compact footprint.
Conclusion
Maximizing boiler efficiency is a multifaceted endeavor that requires a comprehensive approach encompassing maintenance, operational practices, technology upgrades, monitoring, and cultural shifts. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, boiler users can achieve significant energy savings, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and enhance the overall sustainability of their operations.
While the upfront costs of implementing some of these strategies may seem daunting, the long-term benefits in terms of reduced energy costs, improved operational efficiency, and environmental stewardship often outweigh the initial investment. Additionally, many regions offer incentives, rebates, or tax credits for energy-efficient upgrades, further enhancing the financial viability of these initiatives.
Ultimately, maximizing boiler efficiency is not just a matter of cost savings; it’s a responsible and forward-thinking approach to sustainable industrial operations. By embracing energy efficiency, boiler users can contribute to a more sustainable future while maintaining a competitive edge in an ever-evolving industrial landscape.

