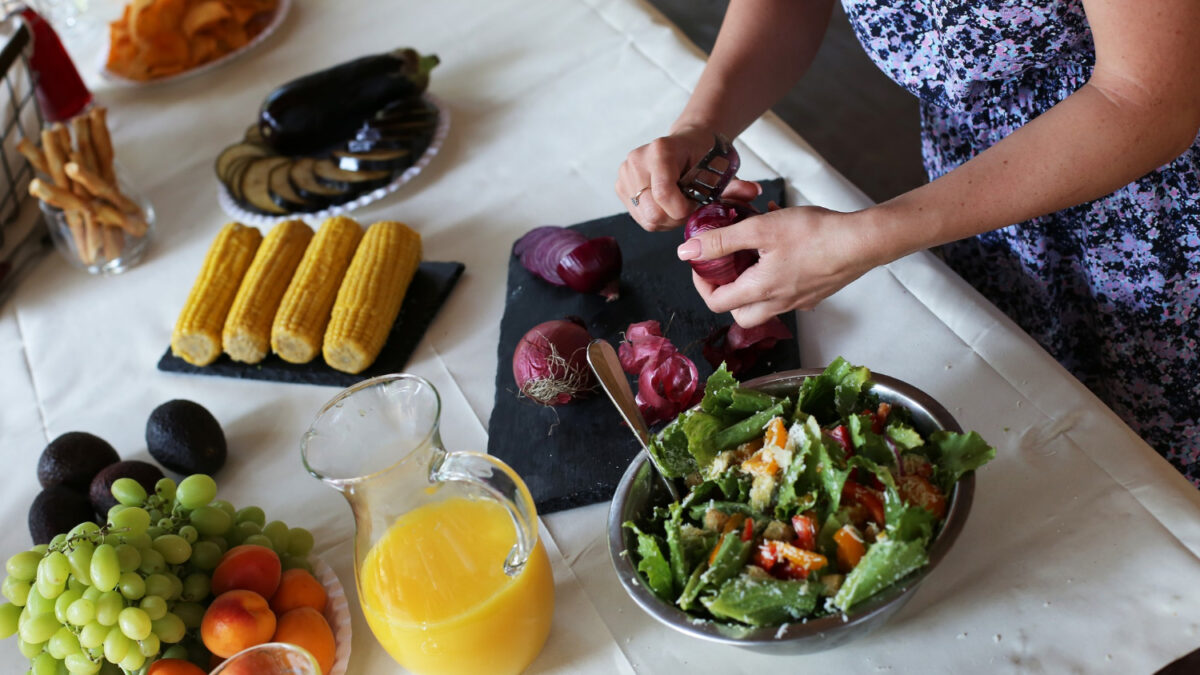The Mediterranean diet has long been celebrated not only for its delicious flavors but also for its profound health benefits. Originating from the regions surrounding the Mediterranean Sea, including Greece, Italy, and Spain, this dietary pattern has garnered attention from nutritionists, health experts, and food enthusiasts worldwide. Health and nutrition are central to its principles, emphasizing the consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and olive oil while limiting red meat and processed foods. Let’s delve into the intricate details of this culinary tradition and explore the science-backed reasons behind its remarkable health advantages.
Understanding the Mediterranean Diet: An Overview
The Mediterranean diet is characterized by an abundance of fresh, locally sourced ingredients that form the foundation of every meal. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and olive oil take center stage, while moderate amounts of fish, poultry, dairy, and red wine are also included. The emphasis lies on whole, minimally processed foods, while refined sugars, saturated fats, and processed meats are limited.
Nutrient-Rich Components: The Key to Health
What sets the Mediterranean diet apart is its rich array of nutrients that contribute to overall well-being. Let’s break down some of the essential components:
- Olive Oil: The cornerstone of Mediterranean cuisine, olive oil is rich in monounsaturated fats, particularly oleic acid, which is known for its heart-healthy properties. It also contains powerful antioxidants that help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in the body.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Loaded with vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants, fruits and vegetables play a pivotal role in the Mediterranean diet. These nutrient-dense foods help lower the risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease, stroke, and certain cancers.
- Whole Grains: Whole grains like barley, bulgur, quinoa, and whole wheat provide complex carbohydrates, fiber, and essential nutrients. They contribute to satiety, regulate blood sugar levels, and promote digestive health.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are staples in the Mediterranean diet, offering a rich source of plant-based protein, fiber, and micronutrients. They are associated with improved weight management, reduced cholesterol levels, and better blood sugar control.
- Fish and Seafood: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are consumed regularly in the Mediterranean diet. These healthy fats support heart health, reduce inflammation, and promote brain function.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, pistachios, and seeds like flaxseeds and chia seeds are packed with healthy fats, protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They offer numerous health benefits, including improved cholesterol levels, reduced inflammation, and enhanced cognitive function.
- Red Wine: Consumed in moderation, red wine is a hallmark of the Mediterranean diet. It contains antioxidants like resveratrol, which may offer protective effects against heart disease and age-related decline.
Health Benefits Backed by Science
Numerous studies have demonstrated the myriad health benefits associated with the Mediterranean diet. Here are some of the compelling findings:
- Heart Health: The Mediterranean diet is renowned for its ability to reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke. It helps lower LDL cholesterol levels, triglycerides, and blood pressure, while increasing HDL cholesterol levels, thereby promoting cardiovascular health.
- Weight Management: With its emphasis on whole, nutrient-dense foods and healthy fats, the Mediterranean diet supports weight loss and weight maintenance. It fosters feelings of fullness, reduces cravings for unhealthy foods, and promotes long-term adherence.
- Diabetes Management: The Mediterranean diet has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, blood sugar control, and overall glycemic control in individuals with diabetes. Its emphasis on low-glycemic-index foods and healthy fats helps stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Cancer Prevention: Studies suggest that adhering to the Mediterranean diet may lower the risk of certain cancers, including breast, colorectal, and prostate cancers. The abundance of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds in fruits, vegetables, and olive oil may play a protective role.
- Brain Health: The Mediterranean diet is associated with better cognitive function, memory, and mood. Its nutrient-rich components, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants, support brain health and may reduce the risk of age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
Practical Tips for Adopting the Mediterranean Diet
Incorporating the Mediterranean diet into your lifestyle doesn’t have to be daunting. Here are some practical tips to help you get started:
- Embrace Plant-Based Foods: Make fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds the cornerstone of your meals. Aim to fill half your plate with colorful plant-based foods at every meal.
- Choose Healthy Fats: Opt for olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds as primary sources of fat. Use olive oil for cooking and dressing salads, and enjoy a handful of nuts or seeds as a snack.
- Eat Fish Regularly: Aim to include fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel in your diet at least twice a week. These omega-3-rich foods offer numerous health benefits for heart and brain health.
- Limit Red Meat and Processed Foods: Reduce your intake of red meat, processed meats, and processed foods high in added sugars and unhealthy fats. Instead, prioritize lean sources of protein like poultry, fish, and plant-based proteins.
- Enjoy Meals Mindfully: Take the time to savor and enjoy your meals, paying attention to flavors, textures, and aromas. Eat slowly, chew your food thoroughly, and listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and support overall health. Limit sugary beverages and alcohol, opting for water, herbal tea, or infused water instead.
- Be Active Every Day: Incorporate regular physical activity into your routine, whether it’s walking, cycling, swimming, or yoga. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week to support heart health and overall well-being.
In Conclusion
The Mediterranean diet offers a holistic approach to health and nutrition, emphasizing whole, nutrient-dense foods, healthy fats, and a balanced lifestyle. Backed by scientific research and centuries of culinary tradition, this dietary pattern promotes longevity, vitality, and overall well-being. By embracing the principles of the Mediterranean diet and making simple, sustainable changes to your eating habits, you can reap the myriad health benefits and enjoy a lifetime of delicious, nourishing meals. Cheers to good health and the joy of Mediterranean-inspired eating!