In the realm of health concerns, some conditions manage to fly under the radar, causing subtle yet profound effects on a person’s well-being. Hypothyroidism is one such condition. Often referred to as the “silent epidemic,” hypothyroidism affects millions of people worldwide, and many are unaware of its presence in their lives. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricacies of hypothyroidism, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and lifestyle adjustments.
=> Take the first step towards a healthier you. Click to find out how?
What Is Hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism, in simple terms, is a thyroid disorder where the thyroid gland does not produce sufficient thyroid hormones to meet the body’s needs. The thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped organ located in the neck, plays a pivotal role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, energy production, and body temperature. When it doesn’t function optimally, it can lead to a cascade of health issues.
Causes of Hypothyroidism
Understanding the underlying causes of hypothyroidism is crucial for effective management. There are several factors that can contribute to this condition:
1. Autoimmune Disease (Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis)
The most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and damages the thyroid gland. Over time, this damage reduces the thyroid’s ability to produce hormones.
2. Surgical Removal of Thyroid
In some cases, individuals may undergo surgery to remove part or all of their thyroid gland, often as a treatment for thyroid cancer or severe thyroid enlargement. This can result in hypothyroidism.
3. Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy, used to treat cancers in the head and neck area, can inadvertently damage the thyroid gland, leading to hypothyroidism.
4. Medications
Certain medications, such as lithium, amiodarone, and interferon-alpha, can interfere with thyroid hormone production and cause hypothyroidism.
5. Iodine Deficiency
Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones. A diet lacking in iodine can lead to hypothyroidism, although this cause is rare in developed countries due to iodized salt.
=> Learn about success stories from individuals who have conquered hypothyroidism.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Hypothyroidism is notorious for its ability to mimic other health issues, making it challenging to diagnose. However, there are several common symptoms that can serve as red flags:
- Fatigue: Overwhelming tiredness and lack of energy, often unrelieved by sleep.
- Weight Gain: Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight.
- Cold Sensitivity: Feeling excessively cold, even in warm environments.
- Dry Skin and Hair: Skin may become dry and hair brittle.
- Muscle and Joint Pain: Unexplained muscle and joint pain.
- Constipation: Sluggish bowel movements and constipation.
- Depression: Feelings of sadness and depression.
- Memory Problems: Difficulty concentrating and memory lapses.
- Menstrual Irregularities: Changes in menstrual cycle for women.
- Hoarseness: Changes in the voice.
It’s important to note that symptoms can vary from person to person, and some individuals may experience only a few of these symptoms, making diagnosis even more challenging.
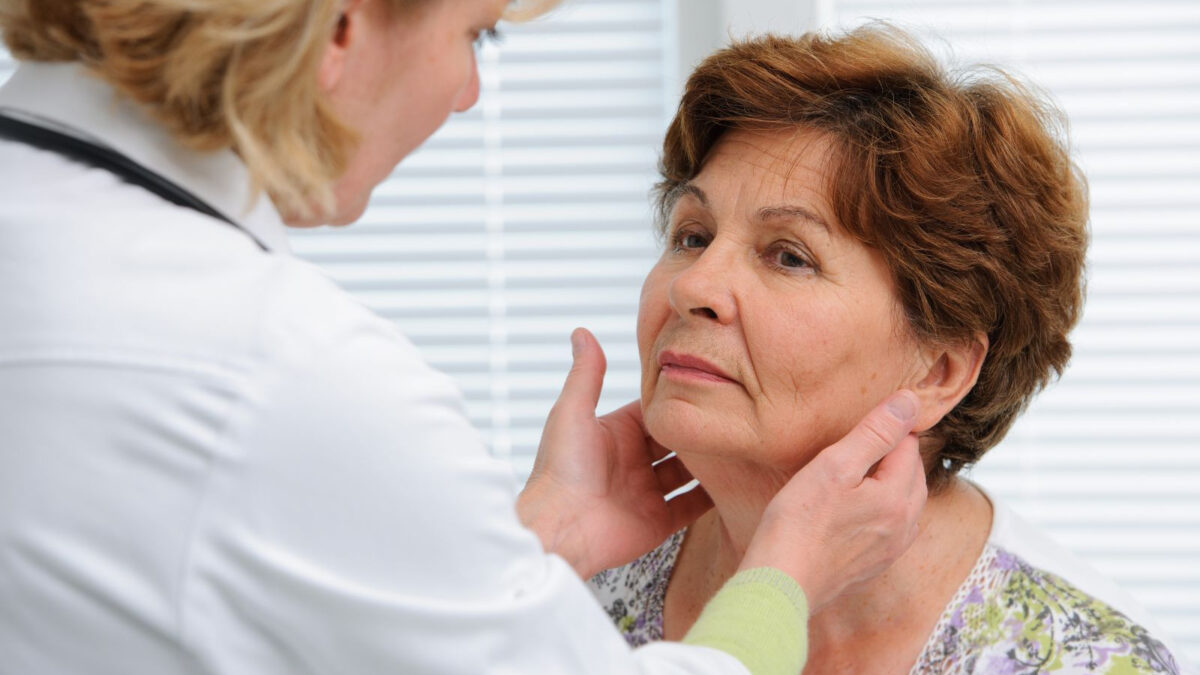
Diagnosis and Testing
If you suspect you have hypothyroidism, it’s crucial to seek medical advice. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. The primary blood test used to diagnose hypothyroidism is the Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) test. Elevated TSH levels are indicative of an underactive thyroid.
Other Tests May Include:
- Free T4 Test: Measures the amount of unbound T4 hormone in the blood.
- Thyroid Antibody Tests: To identify autoimmune causes of hypothyroidism.
- Ultrasound: To visualize the thyroid gland’s size and structure.
- Radioactive Iodine Uptake Test: Measures how much iodine the thyroid takes in.
Treatment Options
Hypothyroidism is a manageable condition, and treatment aims to restore thyroid hormone levels to normal. The most common treatment is hormone replacement therapy using synthetic thyroid hormones like levothyroxine. These medications help compensate for the hormone deficiency in the body.
Lifestyle Adjustments
In addition to medication, certain lifestyle changes can help manage hypothyroidism effectively:
1. Diet
A balanced diet rich in nutrients, especially iodine and selenium, is essential for thyroid health. Foods like fish, dairy, nuts, and whole grains can provide these nutrients.
2. Exercise
Regular physical activity can help boost metabolism and alleviate some hypothyroidism symptoms, such as weight gain and fatigue.
3. Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate hypothyroidism symptoms. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques like meditation and yoga into your routine can be beneficial.
4. Medication Compliance
It’s crucial to take thyroid medication as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor your thyroid hormone levels and adjust medication as needed.
=> Ready to take control of your thyroid health? Explore our recommended resources here.
Conclusion
Hypothyroidism may be a silent epidemic, but it’s not an insurmountable one. With the right diagnosis, treatment, and lifestyle adjustments, individuals with hypothyroidism can lead healthy, fulfilling lives. If you suspect you may have hypothyroidism or are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned in this article, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
Remember, your health is your most valuable asset, and taking proactive steps to address hypothyroidism can make all the difference in your well-being.