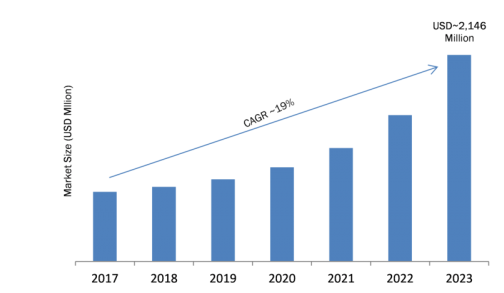
Emerging economies are vast and complicated, with numbers of resellers, millions of branches, and billions of dollars in prospective exchanges. Producers must manage an extensive array of local and global resellers while also balancing the competing requirements of diverse distribution channels. But how can makers handle everything with limited economic knowledge and information? How are they going to seize authority? How will they work with people and advertising while keeping costs low? And, most importantly, how can we make this simple?
The solution lies in flexible, intelligent, yet straightforward software, which a Distributor Management System provides.
What Is Distribution Management All About?
Supervising the flow of products and services or producers to highlight the sale is referred to as distribution management. It is a broad term that covers a variety of behaviors and mechanisms, including wrapping, stock control, storage of goods, distribution network, and logistical support.
The distributor management application is an integral aspect of the overall economy for manufacturers and retailers. Enterprises’ operating margins are determined by how rapidly they can transform their own products. The further they offer, the greater they acquire, implying a brighter future for the organization. A comprehensive distributor consumer management system is also necessary for businesses to flourish, improve their service, and satisfy their customers.
Important Turnovers
The distribution management application is in charge of a company’s supply chain, from contractors and customers to manufacturers and points of sale, including wrapping, stockpiles, storage, distribution, and logistic support.
Adopting a distribution management strategy is critical to a corporation’s economic achievement and long-term viability. However, the distributor management application assists in keeping things in check and clients’ content.
Recognizing Distribution Management
Distribution management is crucial to a firm’s recruiting clients and running a profitable business. Its efficient implementation necessitates impactful control of the project distribution chain. The bigger a corporate entity or, the higher the number of supply points a corporation has, the further it will have to rely on automated processes to handle the allocation system efficiently.
Developed distributor management application entails more than simply transporting goods from point A to point B. It also entails assembling and disseminating necessary details that can define key opportunities in the marketplace and competitive intensity. Most forward-thinking businesses now use their allocation troops to gather marketing information, which is critical in determining their leading advantages.
Commercial distribution (also widely recognized as sales distribution) and outbound logistics are the two main types of transfer (widely known as logistics). Customer support, shipments, storage of goods, stock management, corporate truckload operational processes, wrapping, accepting, quality control, processing facility, storage facility, store location planning, and information processing are all part of the allocation.
The company aims to maximize customer satisfaction by providing raw materials and components and partly and fully final goods at the right moment in the correct circumstance. Direct materials should be planned in line with the global strategic approach.
Distributor Management As an Important Sales Key
The basic principle of supply chain management as a marketing process is that distribution management occurs in an ecological system.
Goods: An item is not always a physical entity; it could also refer to that of a concept, entertainment, or details.
Fee: The benefit of goods and services for both the supplier and the consumer, including quantitative and qualitative measures such as original amount, discounted rates, funding, and the probable answer of current and potential customers.
Advertising: Any interaction used by a vendor to notify, try and convince, or reassure purchasers and prospective customers well about the vendor’s products, assistance, picture, concepts, and the effect they have on the societal structure is considered a promotion.
Configuration: This is the process of ensuring that items are produced, accessible, and visible to end clients or corporate clients in the aim networks or clients where they are needed.
Successful distributor management entails marketing your product while ensuring adequate inventory in networks and handling promotional offers and their differing prerequisites in those streams. It also entails ensuring that a distribution network is effective enough just to keep allocation prices low enough in a particular product or service at the appropriate cost, thus assisting your marketing approach and maximizing profit.
Final Word
The purpose is to achieve productivity and produce crude ingredients or finished goods at the correct time and place in an excellent state. As a result, a Distributor Management Software:
- Performs order fulfillment
- Stock and warehouse management
- Lowering overhead expenses and managerial expenses
- Synchronizes merchandise producers and consumers
- Makes delivery arrangements and manages the payment process
- Produces a Proforma receipt or Negotiable instrument
- Analyzes company data and generates claims
- Makes the company projections, among other things
And this is why the involvement of DMS is critical and, therefore, should be implemented in every organization for the greater good, increased generating revenue, and lower costs.